To achieve long-term sustainability, urban systems must tackle social justice and equity
Inclusivity and understanding past policies and their effects on underserved and marginalized communities must be part of urban planning, design, and public policy efforts for cities.
An international coalition of researchers—led by Georgia Tech—have determined that advancements and innovations in urban research and design must incorporate serious analysis and collaborations with scientists, public policy experts, local leaders, and citizens. To address environmental issues and infrastructure challenges cities face, the coalition identified three core focus areas with research priorities for long-term urban sustainability and viability. Those focus areas should be components of any urban planning, design, and sustainability initiative.
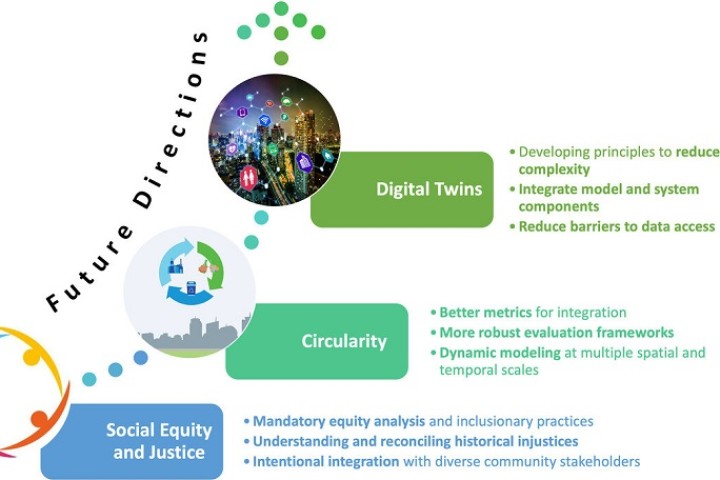
The researchers found that the core focus areas included social justice and equity, circularity, and a concept called "digital twins." The team—which consists of 13 co-authors and scholars based in the U.S., Asia, and Europe—also provided guidance and future research directions for how to address these focus areas. They detailed their findings in the Journal of Industrial Ecology, published in January 2023.
"Climate change has certainly increased the amount and intensity of extreme weather events and because of that, it makes our decision making today critical to the manner in which our economy and our day to day lives can operate," said Joe F. Bozeman III, the lead author and an assistant professor in Georgia Tech's School of Civil and Environmental Engineering. He is also the director of Tech's Social Equity & Environmental Engineering Lab. "Our quality of life can be negatively affected if we don't make good decisions today."
Three core areas of focus to achieve urban sustainability
The researchers' first core focus area, justice and equity, addresses innovations and trends that disproportionately benefit middle and high-income communities. Trends like IoT, "smart cities," and the urban "green movement" are part of a broader push by cities to become more sustainable and resilient. But communities of color and low-income neighborhoods—the same areas often home to environmental contaminations, infrastructure challenges, and other hazards—have often been overlooked.
The researchers' findings showed a consistent trend with marginalized communities across several countries, including Canada, the Netherlands, India, and South Africa. They call for mandatory equity analyses which incorporate the experiences and perspectives of these marginalized communities, and, more importantly, ensure members of those communities are actively engaged in decision-making processes.
"Planning, professional, and community stakeholders," the researchers write in the paper, "should recognize that working together gets cities closer to harmonizing the technological and social dimensions of sustainability."
The second focus area, circularity, addresses resource consumption of staple commodities including food, water, and energy; the waste and emissions they generate; and the opportunities to increase conservation of those resources by boosting efficiencies.
"What we mean by circularity is basic reuse, remanufacturing, and recycling efforts across the entire urban system—which not only includes cities and under resourced areas within those cities—but also rural communities that supply and take resources from those city hubs," Bozeman said. The idea is aligned with the circular economy concept which addresses the need to move away from the resource-wasteful and unsustainable cycle of taking, making, and throwing away.
Instead, the researchers argue, cities should look for ways to improve efficiency and maximize local resource use. That has potential benefits not only for urban areas, but rural communities, too. One example, Bozeman said, is the Lifecycle Building Center in Atlanta. It takes old building supplies and sells them locally for reuse.
"By doing that, they're at the beginning stages of creating an economic system, a regional engine where we share resources between cities and rural areas," he said. "We can start creating an economic framework, not only where both sides can make money and get what they need, but something that can actually turn into a sustainable economic engine without having to rely on another state or another country's import or export economic pressures."
To strengthen circularity and make it more robust, the researchers call for more expansive metrics beyond measuring recycling rates and zero waste efforts, to include other parts of the supply chain that may yield new ideas and solutions.
The third focus area, digital twins, addresses the development of automated technologies in smart buildings and infrastructure, such as traffic lights to respond to weather and other environmental factors.
"Let's say there's a heavy rain event and that the rainwater is being stored into retainment," said Bozeman. "An automated system can open another valve where we can store that water into a secondary support system, so there's less flooding, and that can happen automatically, if we utilize the concept of digital twins."
Creating a new urban planning model
The research came about as part of the mission of the Sustainable Urban Systems Section of the International Society for Industrial Ecology, which aims to be a conduit for scientists, engineers, policymakers, and others who want to marry environmental concerns and economic activity. Bozeman is a board member of the Sustainable Urban Systems Section.
"In that role, part of we do is set a vision and foundation for how other researchers should operate within the city and urban system space," he said.
For urban sustainability, engineers and policy makers must come to the table and make collective decisions around social justice and equity, circularity, and the digital twins concepts.
"I think we're at a really critical decision point when it comes to engineers and others being able to do work that is forward looking and human sensitive," said Bozeman. "Good decision making involves addressing social justice and equity and understanding its root causes, which will enable cities to create solutions that integrate cultural dynamics."

